Visualizing the Continuity of Asian Trade Networks in Sixteenth-Century Japanese Nanban Screens
Discussion of Japanese nanban screens and teaching continuity in the sixteenth-century Indian Ocean.
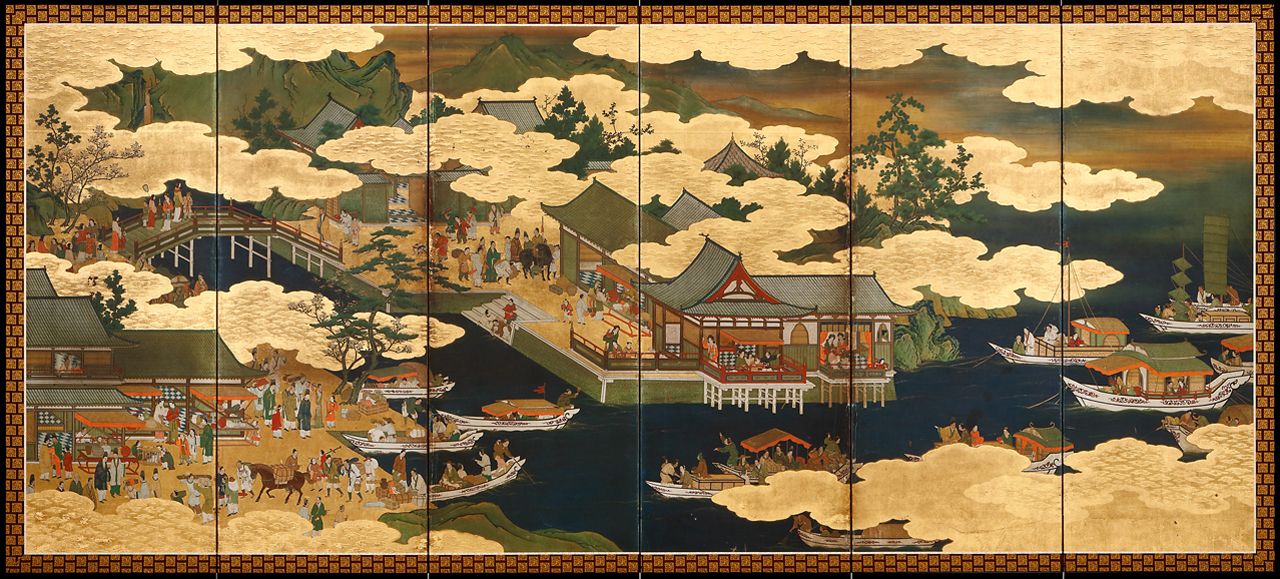

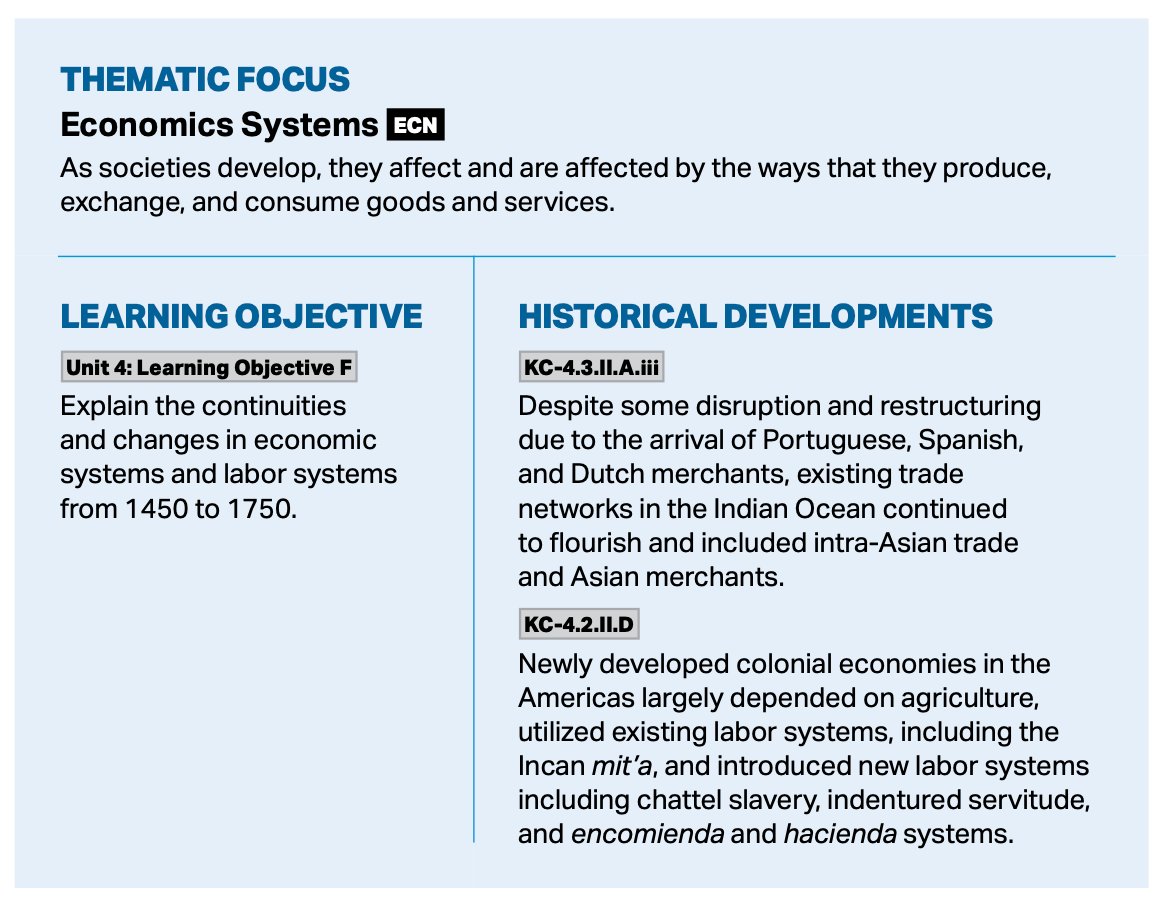
When we teach about the arrival of Europeans in the Indian Ocean in the sixteenth century, it’s easy to get caught up in how Europeans changed exchange patterns. The reality is that most economic, cultural, and political patterns stayed the same, but how do we show students continuities?
The Source
This Content is for Subscribers on the Buy Me Lunch and Buy Me Dinner tiers
SubscribeAlready have an account? Log in