“Foreigners Serve as Our Teachers”: Teaching Nineteenth-Century Qing Reforms
Discussion for teaching Chinese self-strengthening
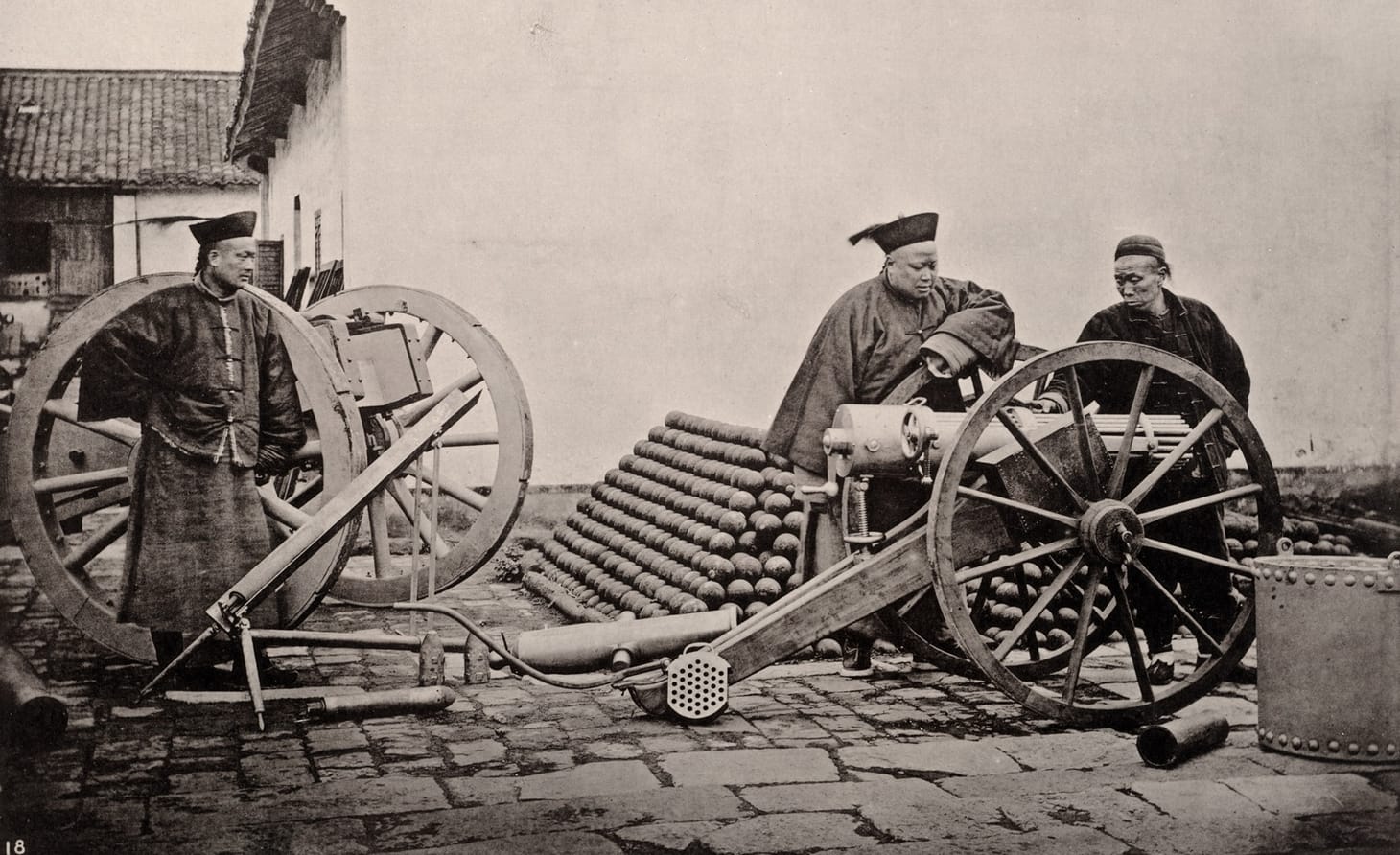

In the previous short post, I discussed how the Ottomans reformed their social structures during the nineteenth century. We can compare Ottoman reforms to Qing reforms. In both cases, some bureaucrats supported reform and others opposed it. By looking at the source below, students can begin to understand both views on reforms.
The Source
This Content is for Subscribers on the Buy Me Lunch and Buy Me Dinner tiers
SubscribeAlready have an account? Log in



