“Zapata spoke Nahuatl”: Indigenous Mexicans Participating in the Mexican Revolution
A discussion of how to teach the participation of Indigenous peoples in the Mexican Revolution.

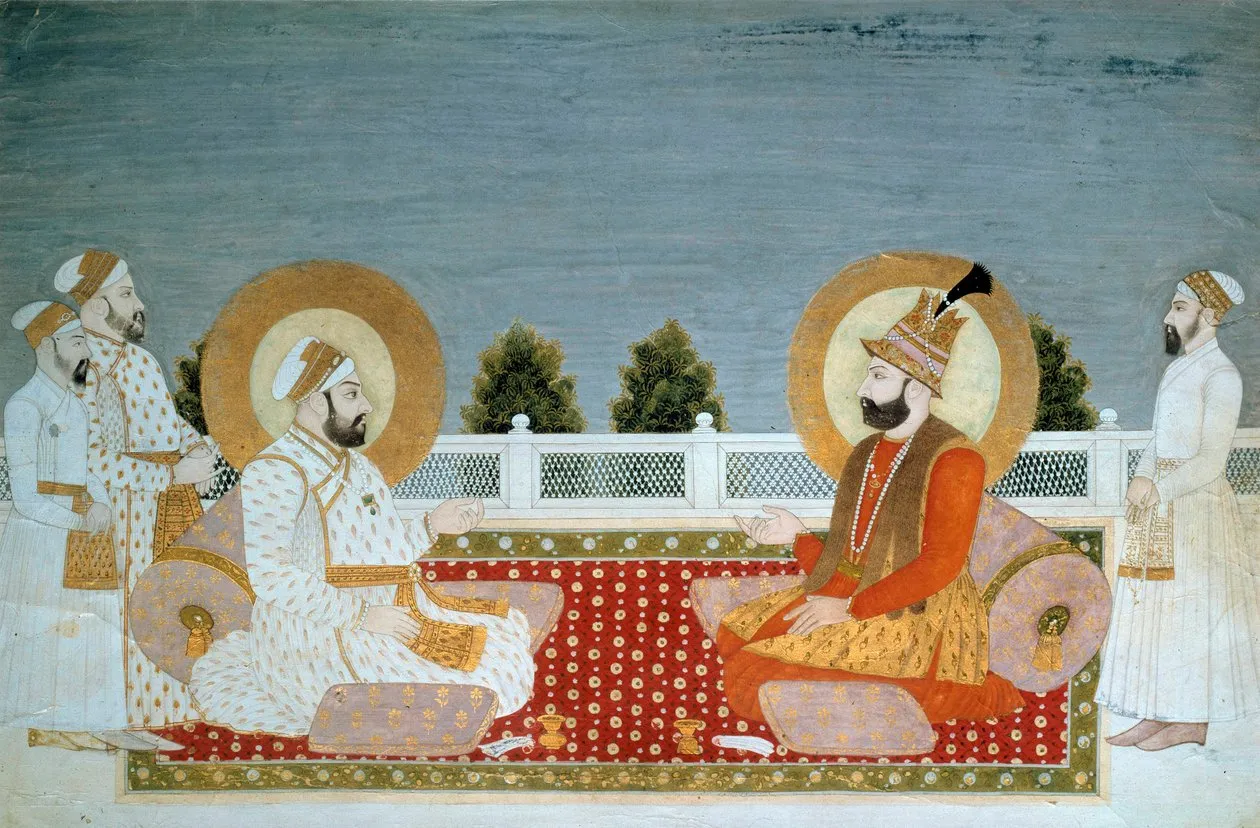
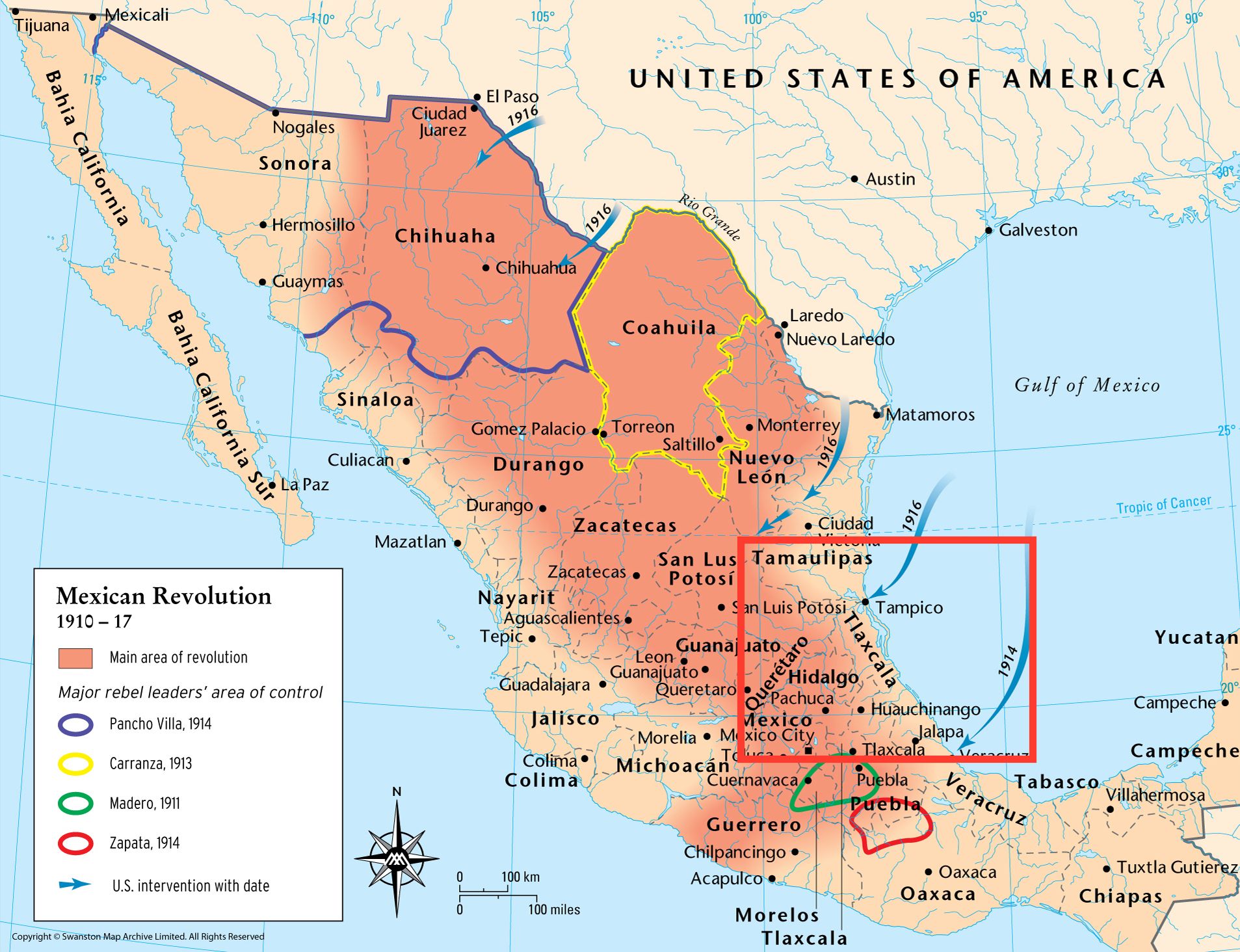
The Mexican Revolution has long been one of my favorite topics to teach in a unit on twentieth-century world history. Instead of beginning in Europe with the causes of the Great War, I like having students compare the Mexican and 1911 Chinese revolutions to decenter Europe’s influence at the start of the century. As I thought about this series on Indigenous Americans, I realized that despite Indigenous Americans being about a third of the Mexican population at the start of the century, world history textbooks rarely mention how they participated in the revolution. Textbooks focus on the class and gender dynamics of the revolution. When it comes to race or ethnicity, there are only occasional references to how land reform benefitted Indigenous Mexicans. Voyages in World History is the only textbook discussing how Indigenous Mexicans participated in the war. Based on what’s in the textbooks, it’s as if Indigenous peoples sat on the sidelines during the Mexican Revolution and waited for an outcome.
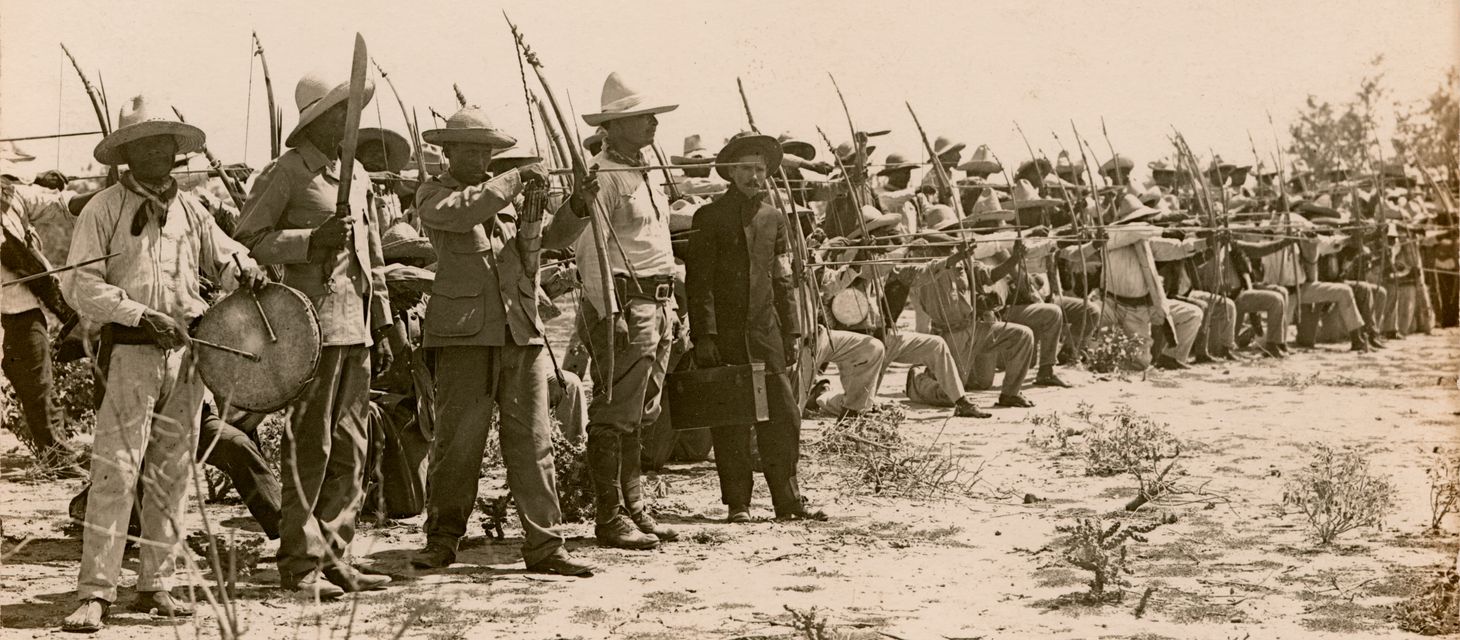
As I researched the topic, I quickly realized that Indigenous Mexicans participated in the revolution. We have many descriptions and photographs of Indigenous soldiers fighting. Even more surprising was that they supported multiple factions in the revolution. Indigenous groups often fought against one another. Instead of thinking about Indigenous Americans as simply the victims of conquest or reflexively resisting oppression, Indigenous American participation in the Mexican Revolution highlights how they had adapted to Mexican society and participated in the same political processes that all Mexicans were involved in from 1910 to 1920.
This content is for Paid Members
Unlock full access to Liberating Narratives and see the entire library of members-only content.
SubscribeAlready have an account? Log in



